In the world of software design, establishing an effective testing strategy is essential for creating high-quality and stable software. This article explores the concept of the test pyramid in detail and examines why it matters and how developers use it during software design.
Test Pyramid: Structure and Purpose
The test pyramid is a testing strategy that visualizes different types of tests in a triangle-shaped pyramid. At the base of the pyramid are the broad, low-level tests (unit tests), while at the top are fewer, but higher-level tests (UI tests, integration tests).
- At the base are broad, low-level tests (unit tests),
- In the middle are component and service tests,
- At the top are a small number of high-level tests (UI and integration tests).
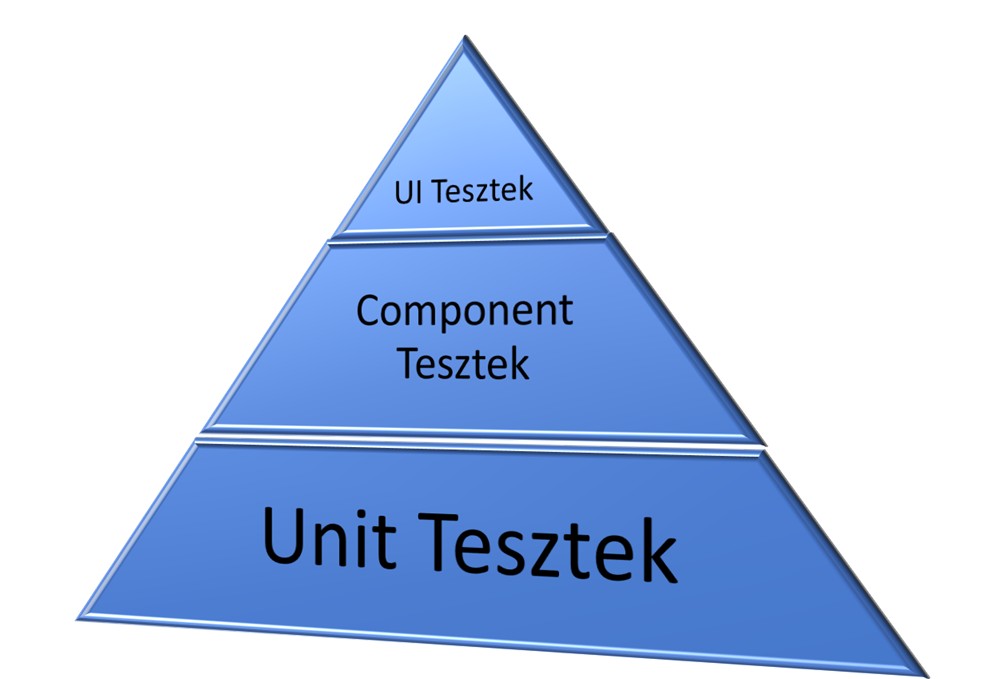
Pyramid Layers
- Base: Unit Tests
- Middle: Component Tests and Service Tests
- Top: UI Tests and Integration Tests
Why Is the Test Pyramid Important?
Cost-Effective Testing
The core principle of the test pyramid is to perform most tests at the lowest level—unit tests. These are fast to run, easy to maintain, and help detect bugs early in the development process, making testing more cost-efficient.
Fast Feedback and Early Bug Detection
Low-level tests, especially unit tests, provide developers with quick feedback about their code. Early detection of issues reduces fix times and helps avoid delays in the development process.
Ensures a Reliable Foundation
Unit and component tests form the foundation of the software. If these pass consistently, higher-level tests are also more likely to succeed. The test pyramid helps ensure the software is built on a stable base.
How to Apply the Test Pyramid?
Unit Tests
Aim to test small, isolated parts of the codebase—such as functions or classes. These tests are usually automated and written by developers.
Component Tests
These verify the interaction between different units (e.g., classes or modules). They help ensure that more complex parts of the application work correctly together.
Service Tests
Service tests cover broader software areas, such as APIs or backend services. They often run in an integration environment to simulate real-world interactions.
UI Tests
These test the user interface of the application. Their goal is to improve user experience and validate UI behavior in a browser or frontend environment.
Example of the Test Pyramid: Web Application
- Unit Tests:
Test individual JavaScript functions and components. - Component Tests:
Verify the correct behavior of frontend components (e.g., React components). - Service Tests:
Check APIs and backend services. - UI Tests:
Simulate user interactions in the browser to test the UI.
Final Thoughts
The test pyramid is a powerful tool for planning and optimizing a testing strategy. By focusing most of the testing effort on the lower levels, we can increase test efficiency and reduce the risks associated with late-stage bug detection. The test pyramid helps balance different levels of testing and contributes to the development of high-quality, stable software.
#QA #softwaretesting #testing #testpyramid #teststrategy

